Articles > Tutorials
How To Configure Your Wired / Wireless Router:
Routers are commonly known to the public as a way of sharing an internet connection with one or more computers. What most people don't realize is that a router is a very complex piece of equipment capable of much more. One of the more useful things that I like routers for is their built in firewall's. Most routers have a built in firewall and web based configuration page that lets you modify the settings of your router. This configuration page is normally accessible from any internet browser. Some of the more advanced routers with have a web based and a telnet configuration page. Some only have telnet. Regardless of with kind of router you have, you will need to determine the ip address of your router.
Step 1: Locating Your Router's IP address
First you have to know what an ip address looks like. An IP address is four sets of numbers separated with periods. Each set is a number between 1 and 254, and since you have a router it will probably start with 192.xxx.xxx.xxx or 10.xxx.xxx.xxx (although it could be any combination of numbers).
Windows 2000 / XP:
Go to Start Menu > Run > Type "cmd". Then at the command window type "ipconfig" and press enter. Write down the IP address and the gateway.
Windows 95 / 98 / ME:
Go to Start Menu > Run > Type "command" then push enter. At the command windows type "ipconfig" and then push enter. Then write down the IP Address and the gateway.
The IP address of your router is the address listed as the "Default Gateway". Save the address listed as "IP Adress" in case you need it later.
Step 2: Connecting To Your Router
Most routers that you can purchase from an electronics or office supply store are web based. Theses are the easiest to configure. Routers that are for large scale businesses tend to be telnet based or web and telnet based. Telnet based routers are normally hard to configure and have more options.
Note: For the rest or this tutorial the ip address 192.168.1.1 is going to be used as the ip address of the router. Anywhere you see 192.168.1.1 please substitute your router's ip address.
Web Based Routers (Most Common)
Open up your favorite internet browser and type in this url http://192.168.1.1 (substitute your router's ip address) and then press enter. This should prompt you for a username and password if you typed in the address of your router correctly.
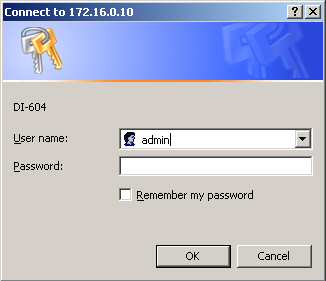
If it doesn't you may have a telnet based router. At the prompt you can normally enter "admin" as the username and leave the password blank, then press enter. If that doesn't work read the following table. If those don't work either refer to your routers documentation.
* (blank) means don't enter anything. Don't type in "(blank)"
** Serial numbers are normally located on the bottom of the router.
*** Located on the bottom.
Telnet Based Routers
To connect to a telnet based router you can not use an internet browser. You can connect to it using any telnet client. Here are two choices I recommend:
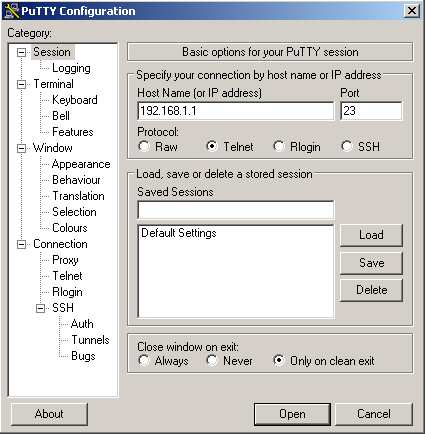
1) Putty is a very cool telnet client program. It is fairly easy to use and free. Just download it here and open it. Then select "telnet", enter your router's ip address and push ok.
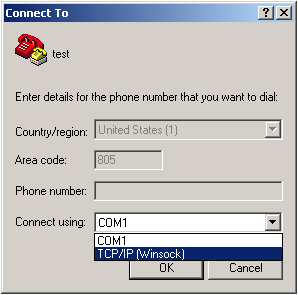
2) HyperTerminal can also be used. Hyperterminal is part of Windows. Go to Start > Run > type "hypertrm". At the first screen type in any name and then push "ok". At the second screen click on the box that says "Connect Using" and select "TCP/IP"
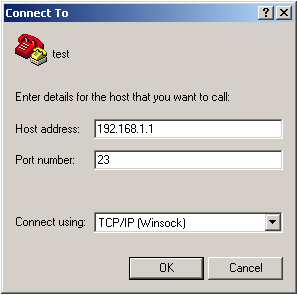
At the next screen type in your router's ip address and push ok
Step 3: Configuring Your Router
Terms you need to know:
IP Address: The address by which a device or computer is referred to on a network that is using TCP/IP.
Dynamic IP Address : An address that changes. This address is normally passed out by a DHCP server.
Static IP Address : An address that does not change. This address is normally passed out by an ISP or network administrator.
PPPoE: This is the protocol of most DSL providers. If you have DSL chances are that you need to configure your router for PPPoE. This normally requires a username (email address) and password.
DHCP Server: A device or computer that assigns ip addresses to other computers or devices.
DNS Server: A device or computer that converts names to their associated ip address.
Local Area Network (LAN): A group of computers that are connected together. Normally located inside the same building.
Wide Area Network (WAN): A large public network consisting of many servers. This normally refers to the internet.
Port: The technical name for a "door" into a device or computer. one device may have one address, but thousands of ports. An open port is like saying the "door" is open.
MAC Address: This is an address that is built into the hardware of a device. This address is not dependent on any specific protocol. The MAC address of a device does not normally change.
This is where things get a little fuzzy. Each company makes their routers a little different. Not only does each company make them different, but each model within each company varies some too. This makes it difficult for me to list all the possibilities. I will show you some pictures with very brief details. (Click on pictures to Enlarge)
This is a typical WAN configuration page:
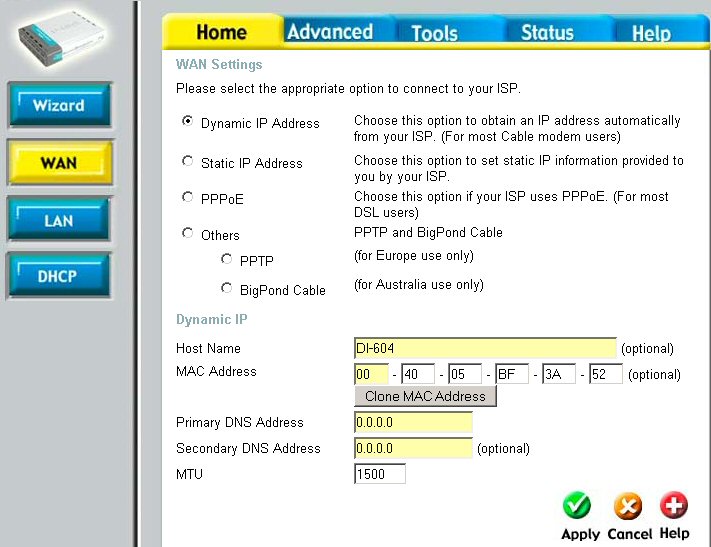
Configuring a Router
Last Updated: 2/14/10How To Configure Your Wired / Wireless Router:
Routers are commonly known to the public as a way of sharing an internet connection with one or more computers. What most people don't realize is that a router is a very complex piece of equipment capable of much more. One of the more useful things that I like routers for is their built in firewall's. Most routers have a built in firewall and web based configuration page that lets you modify the settings of your router. This configuration page is normally accessible from any internet browser. Some of the more advanced routers with have a web based and a telnet configuration page. Some only have telnet. Regardless of with kind of router you have, you will need to determine the ip address of your router.
Step 1: Locating Your Router's IP address
First you have to know what an ip address looks like. An IP address is four sets of numbers separated with periods. Each set is a number between 1 and 254, and since you have a router it will probably start with 192.xxx.xxx.xxx or 10.xxx.xxx.xxx (although it could be any combination of numbers).
Windows 2000 / XP:
Go to Start Menu > Run > Type "cmd". Then at the command window type "ipconfig" and press enter. Write down the IP address and the gateway.
Windows 95 / 98 / ME:
Go to Start Menu > Run > Type "command" then push enter. At the command windows type "ipconfig" and then push enter. Then write down the IP Address and the gateway.
The IP address of your router is the address listed as the "Default Gateway". Save the address listed as "IP Adress" in case you need it later.
Step 2: Connecting To Your Router
Most routers that you can purchase from an electronics or office supply store are web based. Theses are the easiest to configure. Routers that are for large scale businesses tend to be telnet based or web and telnet based. Telnet based routers are normally hard to configure and have more options.
Note: For the rest or this tutorial the ip address 192.168.1.1 is going to be used as the ip address of the router. Anywhere you see 192.168.1.1 please substitute your router's ip address.
Web Based Routers (Most Common)
Open up your favorite internet browser and type in this url http://192.168.1.1 (substitute your router's ip address) and then press enter. This should prompt you for a username and password if you typed in the address of your router correctly.

If it doesn't you may have a telnet based router. At the prompt you can normally enter "admin" as the username and leave the password blank, then press enter. If that doesn't work read the following table. If those don't work either refer to your routers documentation.
Brand |
Default IP Address |
Username |
Password |
|---|---|---|---|
Linksys |
192.168.1.1 |
(blank)* |
"admin" |
Dlink (Older) |
192.168.1.1 |
"admin" |
(blank)* |
Dlink (Newer) |
192.168.0.1 |
"admin" |
(blank)* |
Belkin |
192.168.2.1 |
N/A |
(blank)* |
Netopia |
192.168.1.1 |
"admin" |
(serial number)** |
Motortola |
192.168.2.1 |
"admin" |
"motorola" |
Netgear |
192.168.0.1 |
"admin" |
"password" or "1234" |
Speedstream (SBC) |
192.168.0.1 |
N/A |
(access code)*** |
Speedstream (Other) |
192.168.254.254 |
N/A |
? |
Dell TrueMobile |
192.168.2.1 |
"admin" |
"admin" |
Gateway |
192.168.1.1 |
"admin" |
"admin" |
Asante |
192.168.123.254 |
N/A |
"admin" |
Apple |
Run Utility |
||
US Robotics |
192.168.123.254 |
"admin" |
(blank)* |
Network Everywhere |
192.168.1.1 |
N/A |
"admin" |
Microsoft |
192.168.2.1 |
N/A |
"admin" |
** Serial numbers are normally located on the bottom of the router.
*** Located on the bottom.
Telnet Based Routers
To connect to a telnet based router you can not use an internet browser. You can connect to it using any telnet client. Here are two choices I recommend:
1) Putty is a very cool telnet client program. It is fairly easy to use and free. Just download it here and open it. Then select "telnet", enter your router's ip address and push ok.

2) HyperTerminal can also be used. Hyperterminal is part of Windows. Go to Start > Run > type "hypertrm". At the first screen type in any name and then push "ok". At the second screen click on the box that says "Connect Using" and select "TCP/IP"

At the next screen type in your router's ip address and push ok

Step 3: Configuring Your Router
Terms you need to know:
IP Address: The address by which a device or computer is referred to on a network that is using TCP/IP.
Dynamic IP Address : An address that changes. This address is normally passed out by a DHCP server.
Static IP Address : An address that does not change. This address is normally passed out by an ISP or network administrator.
PPPoE: This is the protocol of most DSL providers. If you have DSL chances are that you need to configure your router for PPPoE. This normally requires a username (email address) and password.
DHCP Server: A device or computer that assigns ip addresses to other computers or devices.
DNS Server: A device or computer that converts names to their associated ip address.
Local Area Network (LAN): A group of computers that are connected together. Normally located inside the same building.
Wide Area Network (WAN): A large public network consisting of many servers. This normally refers to the internet.
Port: The technical name for a "door" into a device or computer. one device may have one address, but thousands of ports. An open port is like saying the "door" is open.
MAC Address: This is an address that is built into the hardware of a device. This address is not dependent on any specific protocol. The MAC address of a device does not normally change.
This is where things get a little fuzzy. Each company makes their routers a little different. Not only does each company make them different, but each model within each company varies some too. This makes it difficult for me to list all the possibilities. I will show you some pictures with very brief details. (Click on pictures to Enlarge)
This is a typical WAN configuration page:

Keywords: configure wireless ip address router
